The world beneath our feet is a hidden realm teeming with life, where intricate networks of roots and rhizomes weave together, sustaining ecosystems and shaping landscapes. Among these underground marvels, the rhizome stands out as a fascinating and versatile structure. This article delves into the world of rhizomes, exploring their unique characteristics, ecological significance, and diverse applications.

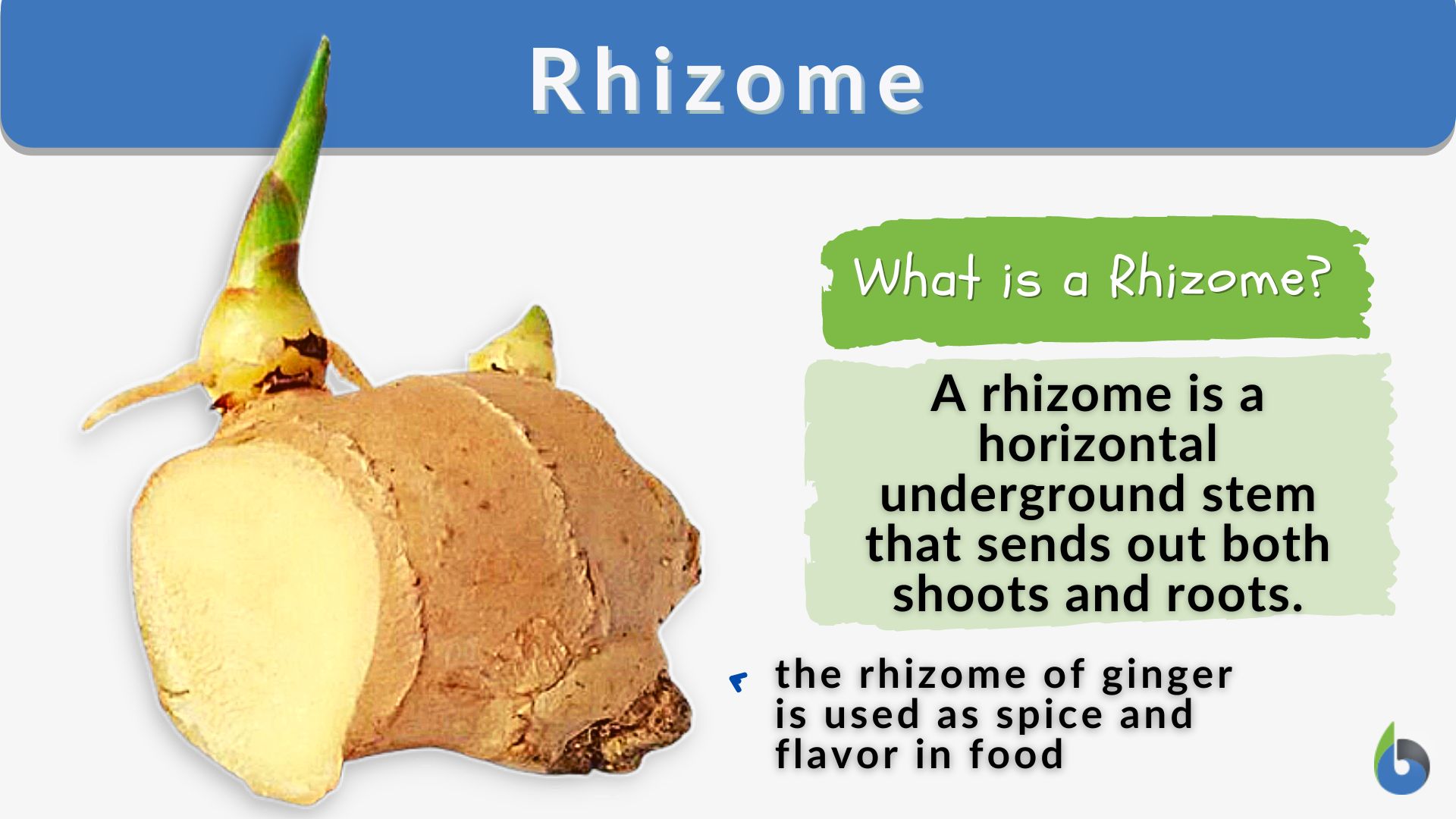
A rhizome is a modified plant stem that grows horizontally underground or along the soil surface. Unlike roots, which primarily function in nutrient and water absorption, rhizomes serve multiple purposes:
Vegetative Reproduction: Rhizomes can produce new shoots and roots at nodes along their length, enabling clonal propagation and rapid spread.
Rhizomes exhibit a wide range of morphological variations, adapting to different ecological niches. Some common features include:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rhizomes-2131103-hero-104c71d3bf924e1cb66e3129ca010287.jpg)
Nodes: These are points along the rhizome where buds, roots, and shoots can develop.
Rhizomes play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems and maintaining ecological balance:
Soil Stabilization: Rhizomes help prevent soil erosion by binding soil particles together.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rhizomes-2131103-03-600783b21f22434da132553af53ef83a.jpg)
Rhizomes have been utilized by humans for centuries, serving various purposes:
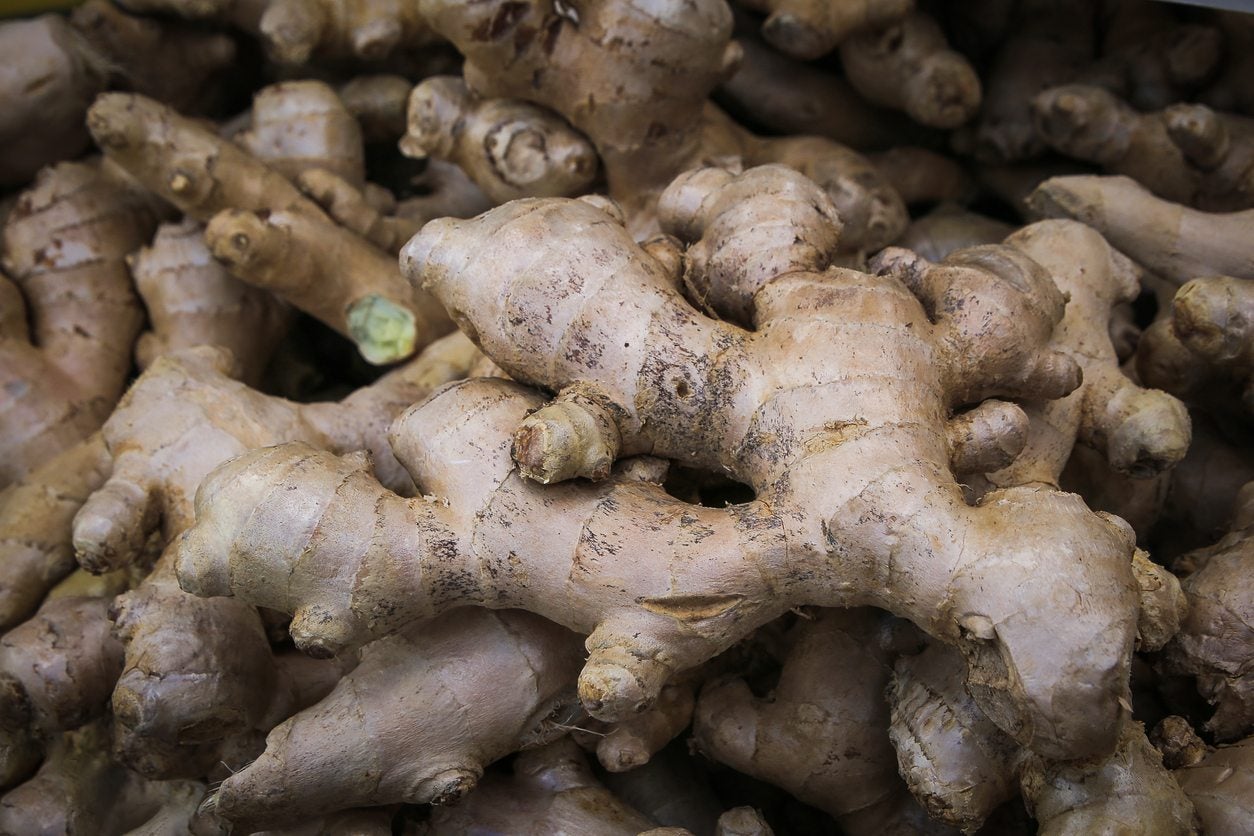
Food: Many rhizomatous plants, such as ginger, turmeric, and bamboo shoots, are valued for their culinary uses.

In horticulture, rhizomes are commonly used for vegetative propagation, allowing gardeners to produce new plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant. Some popular rhizomatous plants used in horticulture include:
Ginger
Rhizomes are remarkable structures that contribute significantly to the biodiversity and ecological health of our planet. Their ability to store energy, reproduce vegetatively, and stabilize soil makes them essential components of many ecosystems. By understanding the biology and ecology of rhizomes, we can better appreciate their importance and harness their potential for various applications, from food production to environmental conservation.
Rhizome Plant
